- 글번호
- 39496581
- 일 자
- 21.04.11
- 조회수
- 730
- 글쓴이
- 연령통합고령사회연구소
- [해외저널] How does a (Smart) Age-Friendly Ecosystem Look in a Post-Pandemic Society?
-
제목 How does a (Smart) Age-Friendly Ecosystem Look in a Post-Pandemic Society?
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(21):8276.
저자 Hannah Ramsden Marston, Linda Shore, P.J. White 발행기관 MDPI AG Series/Report no. Vol. 17, no. 8276 발행일 9 November 2020 키워드 older adults; community; aging; technology; digital; e-health; urban planning; smart ecosystem; gerontechnology; age in place; coronavirus; COVID-19; design hacking; internet of things; human-centered design; smart cities.
Abstract COVID-19 has impacted not only the health of citizens, but also the various factors that make up our society, living environments, and ecosystems. This pandemic has shown that future living will need to be agile and flexible to adapt to the various changes in needs of societal populations.
Digital technology has played an integral role during COVID-19, assisting various sectors of the community, and demonstrating that smart cities can provide opportunities to respond to many future societal challenges. In the decades ahead, the rise in aging populations will be one of these challenges, and one in which the needs and requirements between demographic cohorts will vary greatly.
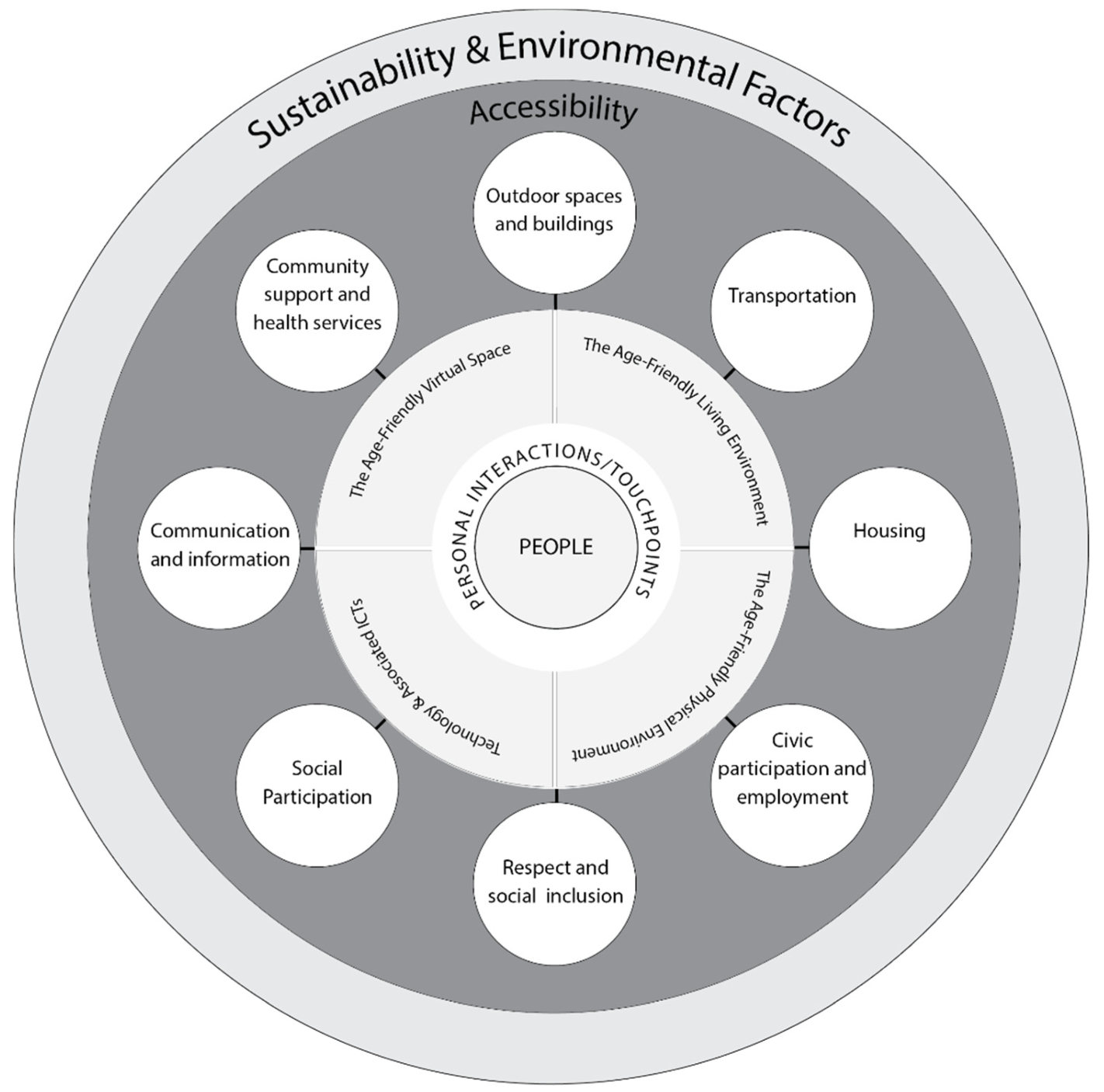
Although we need to create future smart age-friendly ecosystems to meet these needs, technology still does not feature in the WHO eight domains of an age-friendly city. This paper extends upon Marston and van Hoof’s ‘Smart Age-friendly Ecosystem’ (SAfE) framework, and explores how digital technology, design hacking, and research approaches can be used to understand a smart age-friendly ecosystem in a post-pandemic society.
By exploring a series of case studies and using real-life scenarios from the standpoint of COVID-19, we propose the ‘Concept of Age-friendly Smart Ecologies (CASE)’ framework. We provide an insight into a myriad of contemporary multi-disciplinary research, which are capable to initiate discussions and bring various actors together with a positive impact on future planning and development of age-friendly ecosystems. The strengths and limitations of this framework are outlined, with advantages evident in the opportunity for towns, regions/counties, provinces, and states to take an agile approach and work together in adopting and implement improvements for the greater benefits of residents and citizens.
주요 내용 COVID-19는 건강과 함께 우리 사회,생활 환경 및 생태계를 구성하는 다양한 요인에 영향을 미쳤습니다. 이 pandemic은 future living이 사회 인구의 다양한 변화에 적응하기 위해 민첩하고 유연해야 함을 보여주었습니다. 디지털 기술은 COVID-19 기간 동안 커뮤니티의 다양한 부문을 지원하고 스마트 시티가 미래의 많은 사회 과제에 대응할 수 있는 기회를 제공할 수 있음을 보여주면서 중요한 역할을 했습니다. 앞으로 수십 년 동안 고령화 인구의 증가는 이러한 문제 중 하나가 될 것이며 인구 집단 간의 needs와 요구 사항이 크게 달라질 것입니다. 이러한 needs를 충족시키기 위해 미래의 스마트한 고령 친화 생태계를 구축해야 하지만, technology는 고령 친화 도시의 WHO 8 개 영역에 여전히 포함되지 않습니다. 이 연구는 Marston과 van Hoof의 'Smart Age-friendly Ecosystem'(SAfE) 프레임 워크를 확장하고 디지털 기술,디자인 해킹 및 연구 접근 방식을 사용하여 pandemic 이후 사회에서 스마트한 연령 친화적인 생태계를 이해하는 방법을 탐구합니다. COVID-19관점에서 일련의 사례 연구를 탐색하고 실제 시나리오를사용하여'고령 친화적 스마트 생태학(CASE) 개념' 프레임 워크를 제안합니다.
ISSN 1661-7827 (Print) - 1660-4601 (Online)
Link https://doaj.org/article/2dc46676a7c949ee9677febe2644e3ac